Are you in search of the best cycling brakes for your bike? Look no further! This article explores the top options available in the market and discusses their key features, performance, and durability. Whether you’re a professional cyclist or a casual rider, finding the perfect brakes is essential for ensuring your safety and enhancing your riding experience. Say goodbye to squeaky brakes and hello to smooth and reliable stopping power with our guide to the best cycling brakes.
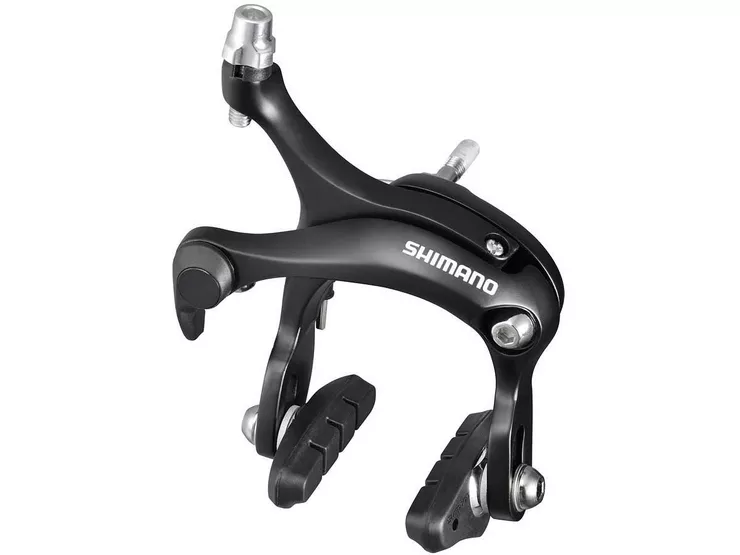
Rim brakes are a popular choice for many cyclists due to their simplicity and affordability. These brakes directly apply pressure to the rim of the wheel to slow down or stop the bike. There are three common types of rim brakes: caliper brakes, cantilever brakes, and V-brakes.
Table of Contents
Toggle1.1 Caliper Brakes
Caliper brakes are the most common type of rim brakes found on road bikes. They feature a single pivot mechanism that allows the brake arms to squeeze the rim, resulting in effective braking power. Caliper brakes are lightweight and provide good stopping power, making them suitable for road cycling where weight and aerodynamics are critical.
1.2 Cantilever Brakes
Cantilever brakes, also known as center pull brakes, are commonly found on cyclocross or touring bikes. They consist of two brake arms that are attached to the frame or fork at separate points. When the brake lever is pulled, the arms move inward, causing the brake pads to press against the rim. Cantilever brakes offer increased clearance for wider tires or mudguards, making them a great choice for off-road or all-weather cycling.
1.3 V-Brakes
V-brakes, also known as linear pull brakes, are widely used on mountain bikes and hybrid bikes. They utilize a pair of brake arms that pull toward each other, generating powerful braking force. V-brakes are easy to install and adjust, and they provide excellent stopping power, making them a reliable option for off-road riding. However, they require the use of special brake levers designed for their cable pull ratio.
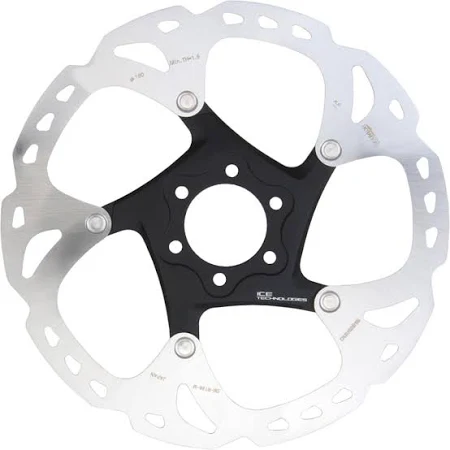
2. Disc Brakes
Disc brakes have gained popularity in recent years due to their superior braking performance and reliability, especially in wet or muddy conditions. Unlike rim brakes, disc brakes use a rotor attached to the wheel hub and a caliper that clamps down on the rotor to slow down or stop the bike. There are two main types of disc brakes: mechanical disc brakes and hydraulic disc brakes.
2.1 Mechanical Disc Brakes
Mechanical disc brakes use a cable to actuate the caliper and apply pressure to the rotor. They are known for their ease of maintenance and affordability. Mechanical disc brakes offer consistent and reliable performance, making them a popular choice for both road and mountain biking.
2.2 Hydraulic Disc Brakes
Hydraulic disc brakes use hydraulic fluid to transmit force from the brake lever to the caliper. They provide excellent modulation and braking power, resulting in precise control and consistent performance. Hydraulic disc brakes are favored by many mountain bikers and are increasingly being used on road bikes for their superior stopping power and responsiveness.
3. Types of Brake Pads
The type of brake pad used in your brakes can significantly impact your braking performance and overall riding experience. Different brake systems require specific brake pads, so it’s essential to choose the right type for your setup. There are two main types of brake pads: rim brake pads and disc brake pads.
3.1 Rim Brake Pads
Rim brake pads are designed to work with rim brakes and provide friction against the rim surface to slow down or stop the bike. They come in various materials, including rubber, cork, and composite compounds. Rim brake pads need to be replaced periodically as they wear down over time and can become less effective. It is crucial to choose the appropriate type of rim brake pad for your rim material to ensure optimal braking performance and prevent excessive wear.
3.2 Disc Brake Pads
Disc brake pads are specific to disc brake systems and are designed to grip the rotor when the brakes are applied. They are available in organic, sintered, or semi-metallic compounds. Organic pads offer excellent modulation and quieter operation but tend to wear down faster. Sintered pads provide outstanding durability and heat resistance but may be harsher on the rotor and can be noisier. Semi-metallic pads strike a balance between the two, offering good performance and durability.
4. Brake Performance Factors
When choosing the best brakes for your bike, several factors contribute to their overall performance. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision that suits your riding needs. The primary performance factors to consider are stopping power, modulation, and heat dissipation.
4.1 Stopping Power
Stopping power refers to the ability of the brakes to bring your bike to a complete stop quickly and safely. It is influenced by multiple factors, including the type of brakes, brake pad material, leverage, and the condition of the braking surface. Disc brakes, especially hydraulic ones, generally provide superior stopping power compared to rim brakes. However, advancements in rim brake technology have resulted in caliper brakes that offer comparable stopping power, especially with high-quality brake pads.
4.2 Modulation
Modulation refers to the brakes’ ability to provide precise control over the braking force. Brakes with good modulation allow you to smoothly vary the amount of braking power applied, giving you better control over your speed. Hydraulic disc brakes are known for their excellent modulation, as the hydraulic system provides consistent and smooth braking power without sudden jolts or jerks. Rim brakes, especially those with high-quality brake pads, can also offer good modulation.
4.3 Heat Dissipation
Heat dissipation is crucial to maintaining consistent braking performance and preventing brake fade, especially on long descents or during heavy braking. Excessive heat can cause the brakes to lose their effectiveness, resulting in reduced stopping power or even total brake failure. Disc brakes, particularly larger rotors and hydraulic systems, are generally better at dissipating heat compared to rim brakes. However, the quality of the brake pads and the materials used can also influence heat dissipation.
5. Durability and Maintenance
Durability and maintenance are essential considerations when choosing brakes, as they can affect the long-term reliability and performance of your bike’s braking system. Factors that influence durability and maintenance include the material and construction of the brakes, pad wear and replacement, and brake adjustment and bleeding.
5.1 Material and Construction
The material and construction of the brakes can significantly impact their durability and performance. High-quality materials, such as aluminum or carbon fiber, are more resistant to corrosion and provide better overall performance. The construction of the brakes, including the pivot points and mounting hardware, should be sturdy and durable to ensure long-lasting performance.
5.2 Pad Wear and Replacement
Brake pad wear is inevitable and will require regular replacement to maintain optimal braking performance. The ease of replacing brake pads and the cost of replacement pads can vary between brake systems. It’s important to consider the availability and cost of replacement pads when choosing your brakes to ensure convenient and affordable maintenance.
5.3 Brake Adjustment and Bleeding
Proper brake adjustment and bleeding are essential for optimal brake performance. Mechanical disc brakes and rim brakes typically require periodic adjustment to ensure proper pad-to-rim or pad-to-rotor alignment. Hydraulic disc brakes may require occasional bleeding to remove air bubbles and maintain consistent performance. Consider the ease of adjustment and bleeding when choosing your brakes, especially if you plan to perform maintenance tasks yourself.
6. Brands
When it comes to brake performance and reliability there is a huge choice, choosing a reputable brand and model can make a significant difference. Here are a few top manufacturers and brands for both rim brakes and disc brakes:
Shimano, Sram, Magura, Campagnola, Hope, Formula, TRP, Avid, and Hayes, do your research and choose the best to suit your budget.
8. Considerations for Different Cycling Disciplines
The choice of brakes can also vary depending on the type of cycling discipline you engage in. Certain factors come into play when considering brakes for road biking, mountain biking, or commuting and touring.
8.1 Road Biking
For road biking, lightweight and aerodynamic rim brakes or hydraulic disc brakes are popular choices. Rim brakes offer a weight advantage and are compatible with most road bike frames and forks. Hydraulic disc brakes provide superior stopping power and modulation, making them ideal for steep descents and fast-paced road riding.
8.2 Mountain Biking
When it comes to mountain biking, disc brakes are the go-to choice due to their superior stopping power and reliability. Hydraulic disc brakes are highly recommended for their precise control and modulation on technical descents and challenging terrain. Mechanical disc brakes can also be a good option for riders on a budget or for those who prefer the simplicity of cable actuation.
8.3 Commuting and Touring
For commuting and touring, reliability and ease of maintenance are key considerations. Depending on the terrain and riding conditions, both rim brakes and disc brakes can be suitable choices. Disc brakes, especially hydraulic ones, offer consistent performance in all weather conditions, making them a reliable option for commuting or long-distance touring.
9. Tips for Choosing the Right Brakes
Choosing the right brakes for your bike involves considering multiple factors. Here are some tips to help you make the best decision:
9.1 Riding Style and Goals
Consider your riding style and goals when choosing brakes. Are you a road cyclist looking for lightweight and aerodynamic options, or are you an off-road enthusiast in need of powerful and reliable braking? Understanding your riding needs will guide you towards the appropriate type of brakes.
9.2 Compatibilities with Bike Frame
Make sure to choose brakes that are compatible with your bike frame and fork. Check the brake mounting options and clearance to ensure a proper fit. Disc brakes may require specific frame and fork specifications, so consider these requirements when making your selection.
9.3 Personal Preferences
Ultimately, personal preferences play an important role in choosing brakes. Some riders may prioritize easy maintenance and affordability, while others may prioritize performance and modulation. Consider what aspects are essential to you and your riding style to find the brakes that best align with your preferences.
10. Conclusion
Choosing the best brakes for your bike can greatly enhance your cycling experience. Rim brakes continue to be a popular choice due to their simplicity and affordability, while disc brakes offer superior performance and reliability, especially in challenging conditions. Consider factors such as stopping power, modulation, heat dissipation, durability, and maintenance when making your decision. Additionally, factor in your cycling discipline, brand and model preferences, and budget considerations. By taking all these factors into account, you can find the perfect brakes to suit your needs and enjoy a safer and more enjoyable ride.